Information Rights Management Service IRMS is an inbuilt Messaging policy feature which is available from Exchange 2013. This inbuilt Messaging policy works along with transport rule to secure all the sensitive email transits that is happening in our organization.
By Using IRMS we will be able to inspect any sensitive email content with help of transport rules, encrypt them and then provide secure access only to the required users.
IRM agents are built in transport agents. But however when we run Get-TransportAgent we will not be able to see the IRM agents visible. Because most of the inbuilt transport agents that come along with the installation are not visible in Get-TransportAgent and they are unmanageable from PowerShell.
IRMS works with the help of ADRMS and informational protected technology which is introduced from Windows Server 2008. ADRMS uses extensible rights markup language (XrML) type certificates to certify users and computers. We need to have AD RMS installed to use this IRM functionality.
By Using IRM following actions can be taken
- We can restrict confidential email to be sent only to the right recipients and other recipients can be blocked.
- Prevent forwarding a confidential message to other recipients.
- Prevent Copying and pasting a confidential message
- Prevent printing a confidential Message
This IRM requires Licensing to work along with ADRMS.When we enable IRM pre-Licensing is enabled by default.
There is a prelicensing agent which acts on the categorizer on the mailbox server in the transport service which attaches a prelicensing in OnRoutedMessage to IRM- protected messages.
So by this prelicensing which is issued by default by the ADRMS to the IRM protected messages end users will be able to access these emails through Outlook in online/offline mode and as well as through OWA, Active sync devices as well.By doing this the client does not need to send a request to the ADRMS for license to access these emails each and every time.
IRM works in the following clients
Manually by Outlook users – By using IRM functionality in Outlook. (This is a client side IRM from outlook and no IRM transport rule from server is triggered in this scenario)
Manually by Outlook Web App users – By using Web-Ready Document Viewing.( This is a client side IRM from outlook and no IRM transport rule from server is triggered in this scenario)
Manually by Windows Mobile and Exchange ActiveSync device – This requires users to connect their supported Windows Mobile devices to a computer and activate them for IRM (This is a client side IRM from outlook and no IRM transport rule from server is triggered in this scenario)
Automatically on Mailbox servers – Works with the help of Transport Protection Rules from server.
Note:
A message which is already IRM protected by any of the client type like Outlook, OWA or Activesync will not be again IRM protected by Transport protection rules since its already protected. IRM purely works with the help of ADRMS encryption so all the client side IRM protection will already be processed if a user tries to use IRM functionality from Outlook or OWA.
IRMS works in the categorizer Mailbox Transport service in the following ways:
RMS Decryption agent – Decrypts the messages to provide access to transport agents for inspection.
Transport Rules agent – An associated IRM transport rule inspects the email and marks the email as IRM protected email and notifies RMS encryption agent
RMS Encryption agent – Identifies the IRM marked messages by transport rule and then encrypts them for protection.
Prelicensing agent – Attaches a prelicensing to this message in OnRoutedMessage to IRM- protected messages by AD RMS cluster.
Journal Report Decryption agent– Decrypts only irm messages with journal reports.
Now let’s see how to enable IRM in Exchange 2013.
Prerequisites to use IRM in Exchange 2013
1) We need to have ADRMS installed in our Environment
Note: We need to have IRMS installed separately on a server. It should not be installed on a server where we have Exchange installed.
Follow the below steps for ADRMS installation.
Open server manager. Go to roles and select ADRMS.
Click next
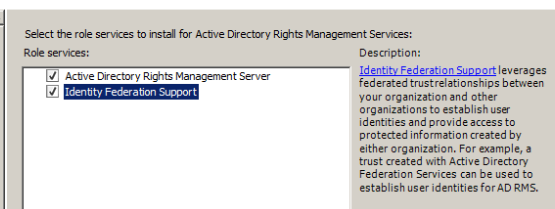
Select federation support as well if you wish to extend ADRMS to federated partners.
Click create new AD RMS cluster
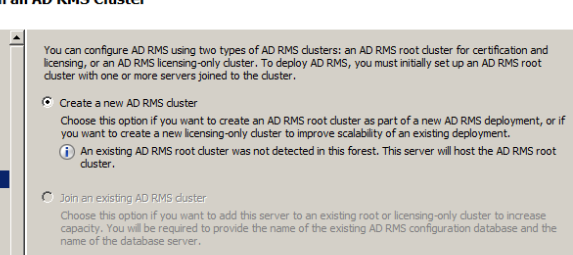
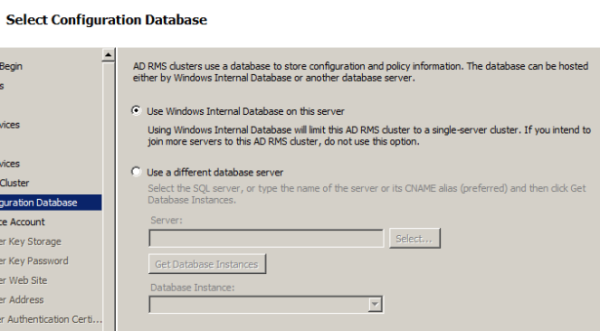
Choose a location to store configuration database
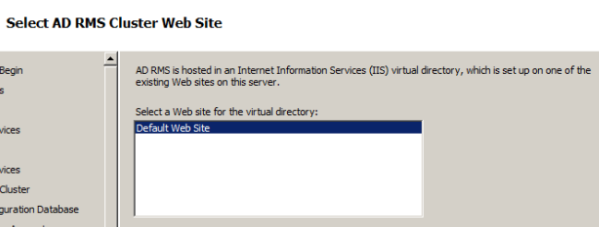
Default website is selected automatically
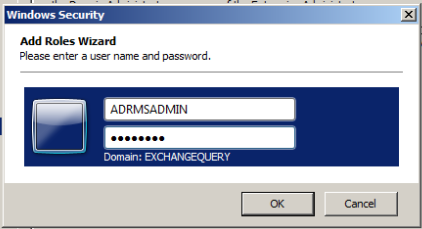
We need to create a separate service account to manage ADRMS
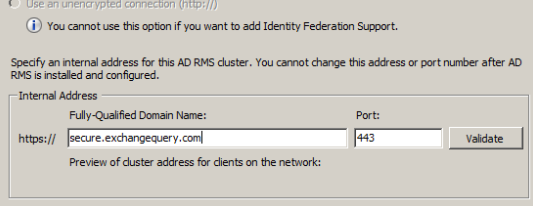
Specify the internal address to be used for ADRMS.
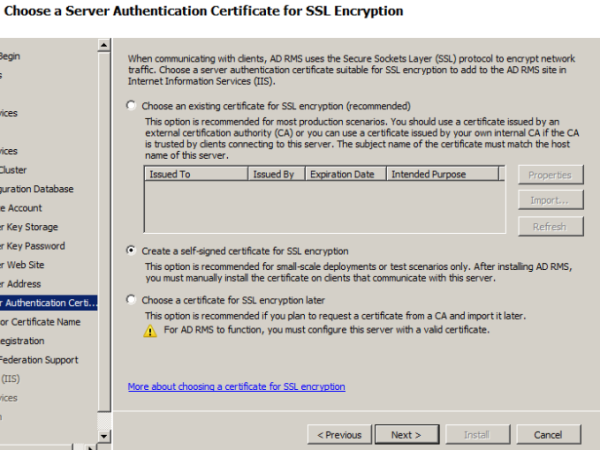
Choose server authentication certificate
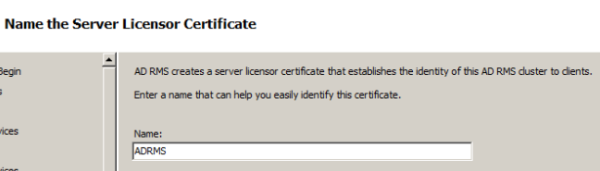
Provide a server licensor certificate which helps to identify the clients
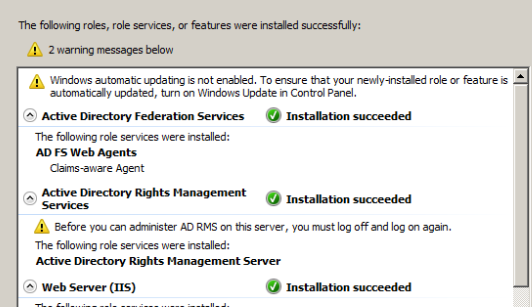
Just navigate through the wizard it’s pretty much easy and complete the installation of ADRMS role.
Note: By default Exchange 2013 IRM features support Microsoft Office file formats. We can extend IRM protection to other file formats by deploying custom protector.
If you need to support additional files then you will need to import custom protector in ADRMS.
For custom protectors refer http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/office/bb802693(v=office.14).aspx
2) Grant access to Exchange servers to use ADRMS for IRM. Perform the following task.
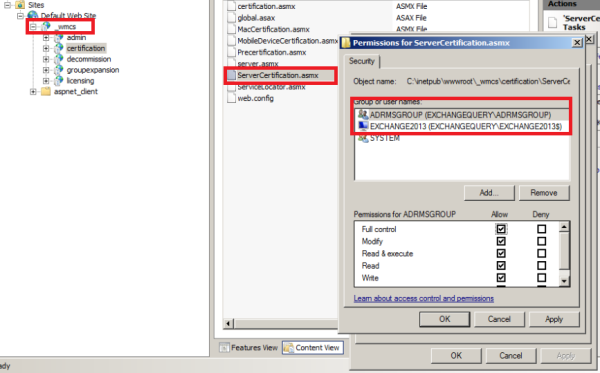
Open IIS – open default Website – Click _wmcs – Select Certification
Switch to content view – right click on servercertification.asmx and click edit permissions ensure that Exchange servers are listed as shown below.
Note: This setting on IIS should be checked on the server where we have installed ADRMS. _wmcs directory will be visible only after we install ADRMS.
3) We need to create a dedicated security group for encryption and decryption of these messages by super admins
Perform the following task
Create a dedicated super user group to be used in AD users and Computers.
Open ADRMS – in security policies select super users and ensure super user functionality is enabled. If not add this user to the group.
4) Run the below commandlets to enable IRM.
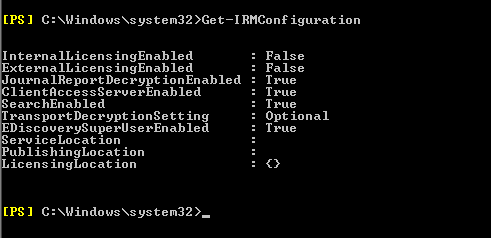
First check the IRM settings by running the below command.
Get-IRM configuration.
To enable on CAS – Set-IRMConfiguration -ClientAccessServerEnabled $true
To Enable for OWA – Set-OWAMailboxPolicy –Identity Default -IRMEnabled $true
For Multimailbox IRM search – Set-IRMConfiguration -SearchEnabled $true
For Licensing Internally – Set-IRMConfiguration –InternalLicensingEnabled $true
For Licensing External users – Set-IRMConfiguration –ExternalLicensingEnabled $true
5) Create an associated transport rule for IRM for mailbox side IRM.
Note: Before creating transport security rules we need to have RMS templates loaded from the ADRMS to use in this rule. To identify the set of RMS template from ADRMS run the below command.
Get-RMSTemplate | format-list
Open EAC – Select Mail flow and select – Rules
Select Apply Rights protection to Messages
Use the Select RMS template dialog box to select a template.
Add any exception if we need to use any exception for few senders.
Below is an example of adding an exception for Administrator. IF any IRM message which matches the Template chosen in IRM for Admin then we can set exception to forward the message to his manager for approval.
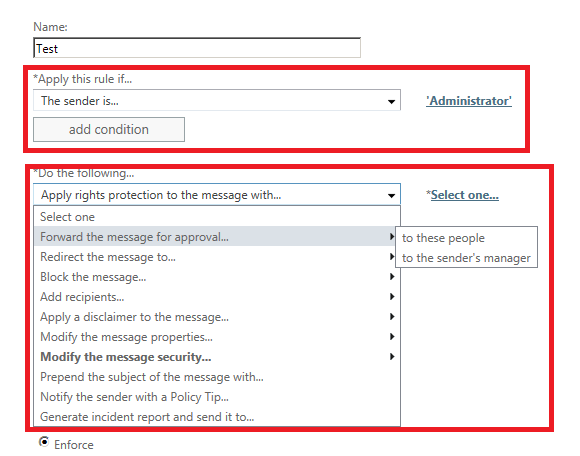
Clicks save and we are done.
Below is an example by using Do not forward template in ADRMS. The Outlook and owa users while composing this message by organizer will receive this type of information as shown below.

Also we can use Test-IRMConfiguration commandlets to check the IRM functionality for a user
Below is an example for testing IRM config for user Adam sent emails.
Test-IRMConfiguration -Sender adams@contoso.com
References: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd638140(v=exchg.150).aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/enus/library/dd298166(v=exchg.150).aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/enus/library/bb125012(v=exchg.150).aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd979798(v=exchg.150).aspx
Sathish Veerapandian