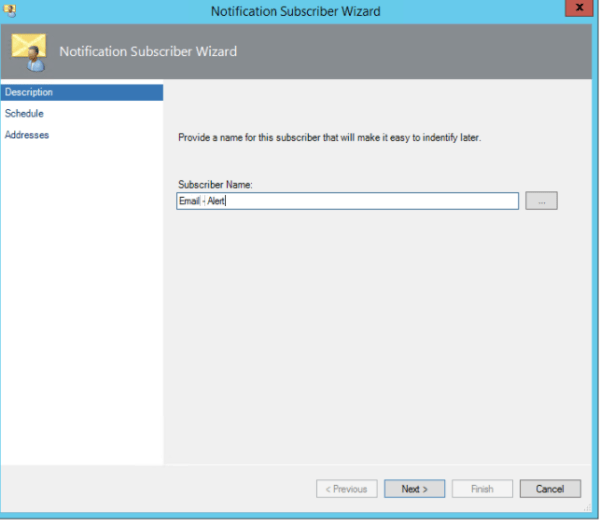
In-order for the users to connect externally from the organization’s network we need to publish the Skype for business services.In this article we will have a look at best ways to publish the Skype for Business Edge servers over the internet.
By doing this the users can participate from external N\W in IM,AV ,web conferencing sessions.
There is lot of confusion in the architectural part of load balancing the Skype for Business Edge servers and cannot be taken as easy deployment. If the SFB deployment is extended to communicate with federated partners, remote connected users and Public Instant Messaging users then a real proper planning of the edge servers deployment needs to be carried over.
If we have 2 or more edge servers deployed in the DMZ they need to be load balanced to equally distribute the load in all the edge interfaces.
In general Microsoft recommends to use a DNS Load Balancer for Edge High Availability.
Load balancing distributes the traffic among the servers in a pool so that the services are provided without any delay.
Below are 3 types of load balancing solution that we can use based on our requirement:
DNS Load Balancer Using NAT :
This is the best recommended approach.
We are actually load balancing each edge services namespace over the internet with multiple A records NATTING them via firewall and then to Edge servers.
These Ip addresses are bound to each services seperately routed to internal individual Ip’s assigned to the external NIC.
Three private IP addresses are assigned to this network adapter, for example 131.107.155.10 for Access Edge service, 131.107.155.20 for Web Conferencing Edge service, 131.107.155.30 for A/V Edge service. These private Ip’s listen individual public IPs Natted from the f/w.
These Ips are not participated in the load balancer and used only for NATing.
They are basically behind a port forwarding firewall which is good.
Advantages of doing this:
1) We are assigning a separate public IP’s for each service and using standard ports. So the remote users will not have any issues on connecting behind their firewall since all are standard ports.
2) Its very good to troubleshoot in analyzing a particular service traffic statistics, Logging and easy to identify the issues with the logs packet capture etc..,
Disadvantages of doing this:
1) The edge services rely on multiple A records with the same name but different IP addresses. So its not service aware configuration and failure detection rate and routing to the available server is not possible.
But still i would go with this option considering the failure detection rate is very minimal in a well planned deployment and strong n/w considering very helpful and easy during any troubleshooting scenarios.
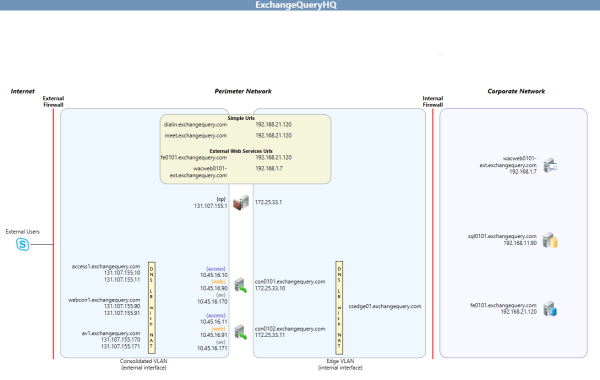
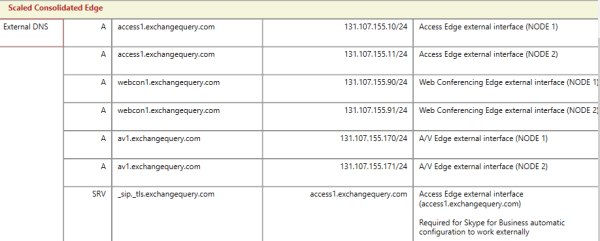
Below is the example of DNS load balancing using NAT
Lets assume i need to load balance 2 edge servers using DNS Load-balancing NAT as per below environment.
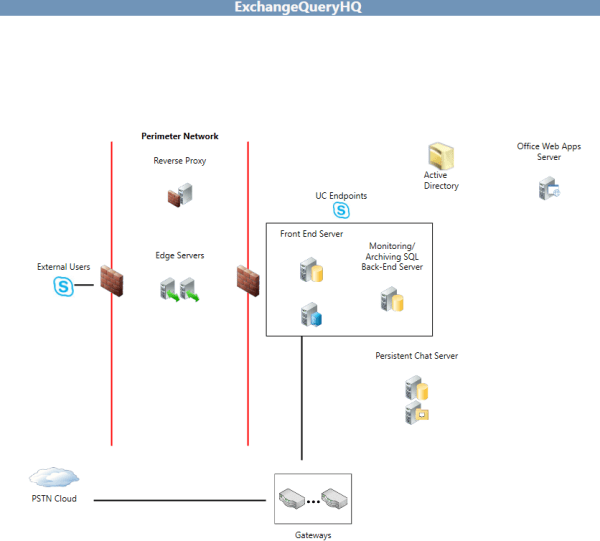
Below is the DNS configuration
DNS Load balancer using Public Ip Addresses:
By doing this we are using one public IP for all 3 services on each server and differentiate them by TCP/UDP port value.
We are directly assigning the public IP’s on the edge servers one of the 2 NIC’s which should be external NIC.
Three private IP addresses are assigned to this network adapter, for example 131.107.155.10 for Access Edge service, 131.107.155.20 for Web Conferencing Edge service, 131.107.155.30 for A/V Edge service.
The Access Edge service public IP address is primary in the NIC with default gateway set to the external Firewall.
Web Conferencing Edge service and A/V Edge service private IP addresses are additional IP addresses in the Advanced section of the properties of Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)
Disadvantages of doing this:
It is not recommended, to use a single public IP address for all three Edge service interfaces.
Though this does save IP addresses, it requires different port numbers for each service.
Access Edge – 5061/TCP
Web Conferencing – 444/TCP
A/V Edge – 443/TCP
These might cause issues for remote users connecting externally from a n/w where their firewall doesn’t allow the traffic over TCP 5061 port.
Having three unique IP addresses will help us in easily doing a packet filtering to identify and resolve the issues.
Hardware load balancing using public Ip Address:
Load balancing is only need for old OCS clients and xmpp, but works fine if both edge server are up. From Lync 2010 Microsoft does not recommends to load balance the Edge services from internet.
We are creating a virtual Ip address for each services that edge serves (Access, WebConferencing, A/V) on the load balancer like F5, KEMP etc..,
Behind this Virtual Ip’s we need to add the edge servers associated for the services.
The main benefit of this is failure detection rate is very quicker since it detects the failure from the server side.
Disadvantages:
1) The A/V services will not see the client’s true IP ( for example in a peer to peer audio call for a user connected from external to internal)
2)Few challenges in configuring the outbound client connections going from the edge to internet (Routing & SNAT)
Thanks & Regards
Sathish Veerapandian
MVP – Office Servers & Services