The Enterprise Vault Office Mail App provides Enterprise Vault features in end users outlook and owa. This works in Integration with the Microsoft Office Mail apps feature.
It is desired that users will try to access archived items via OWA as well when their older items are being archived by a archive system.
The Enterprise Vault Office Mail App does not appear in Outlook or OWA by default.
It requires deployment to users or organizational level and only then they will appear.
In this article i will explain quick steps to perform this action on a environment where we have the Archive enabled for Exchange 2016 users through Enterprise Vault
There are 3 possible methods to perform this action:
1) We can deploy them to individual users.
2) We can deploy them to group of users.
3) We can deploy them to whole organization on the Mailbox Server Organization level.
The main methods are as below:
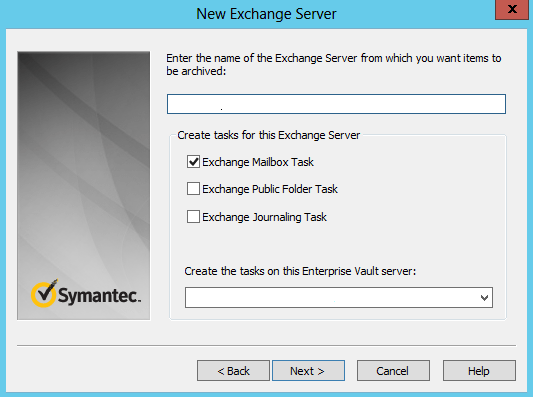
1) We need to deploy the Office Mail App on the Newly introduced Exchange 2016 Server on the org level to EV server.
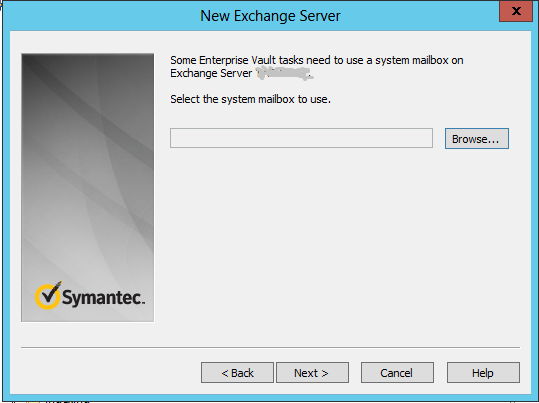
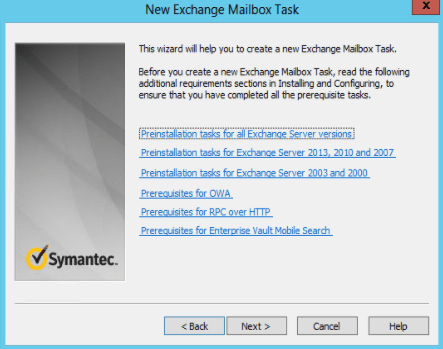
2) Setting up the Enterprise Vault Office Mail App
3) One important note that we need to make is that if we enable this feature on organizational level then this option will appear on all mailboxes including the one’s which has not EV enabled.
4) The same Enterprise Vault server is used for Office Mail App requests from
all users.
The high level steps are as follows :
1)We need to run the PowerShell command New-App in the Exchange Management
Shell on Exchange 2016 Server .
The command requires the following:
2)An Exchange 2016 Server that is enabled for archiving and that you want to enable
for the Office Mail App.
3)The URL of the OfficeMailAppManifest.aspx page from the EV server.
The server that is specified in the URL can be any Enterprise Vault server
in your site can be http or https according to the IIS config on your EV server.
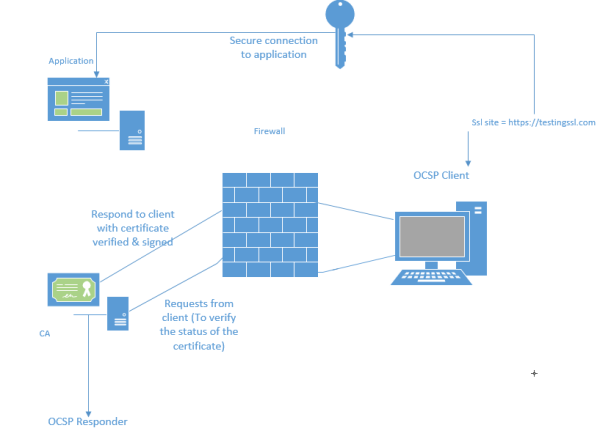
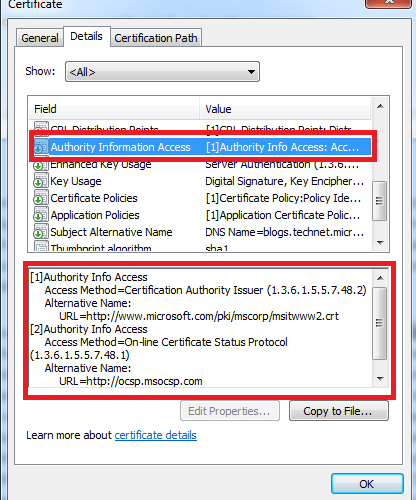
Office Mail Apps must only be served using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). We need to obtain a certificate from a certification authority.
4)The Exchange server sends a request to Enterprise Vault server EV1 to
configure a manifest file.
We need to run the below command to enable this feature on organizational level :
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Web
$Mbx = get-mailbox “mailbox”
New-App -OrganizationApp -DefaultStateForUser:enabled -Url `
(“https://EV_server/EnterpriseVault/OfficeMailAppManifest.aspx?LegacyMbxDn=” +
[System.Web.HttpUtility]::UrlEncode($Mbx.LegacyExchangeDN))
Where:
■ mailbox is the name of a mailbox that is enabled for archiving.
■ EV_server is the name of Enterprise Vault server which has this manifest file in your organization.
When a user access the EV office mail app from the owa or Outlook following things happens:
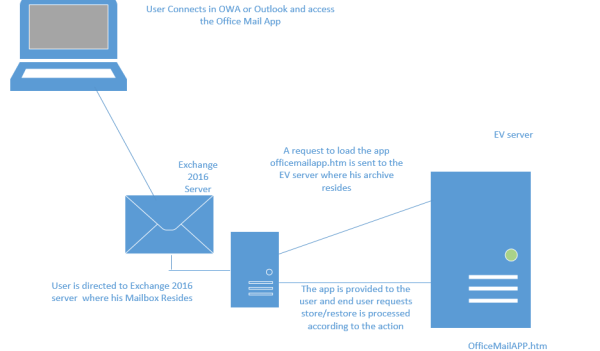
a) Basically this officeMailAppManifest.aspx page from EV server generates a manifest file
for Exchange and sends it to the Exchange 2016 server.
b) The manifest file contains the Office Mail App settings for Exchange.
c) The settings include the URL from which the Office Mail App will be loaded.
d) Later end user will be able to perform his archive action from the Office Mail App.
Below are the steps to enable EV web app for individual users :
$mbx = Get-mailbox mailbox@domain.com | select LegacyExchangeDN
$url = “https://EVurl.com/EnterpriseVault/OfficeMailAppManifest.aspx?LegacyMbxDn=”+ $mbx.LegacyExchangeDN
New-App -Mailbox $mbx.LegacyExchangeDN -Url $url
Later we can verify the end user web app readiness by accessing the Manifest URL from his PC
https://evurl.com/EnterpriseVault/OfficeMailAppManifest.aspx?LegacyMbxDn=/o=MSG/ou=Exchange Administrative Group (FYDIBOHF23SPDLT)/cn=Recipients/cn=mailbox
On accessing the end user should be able to see the XML file an example below.

On a failure to see the XML file will not result in accessing this feature from end user level.
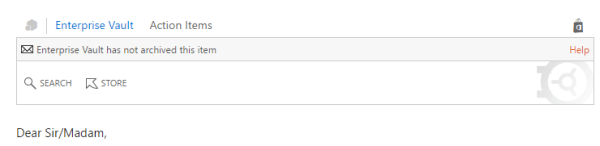
After its enabled this will how it will be displaying for end users on their OWA and Outlook when they open any emails.
Note:
1) This office mail app is not an mandatory feature to be enabled for all users . All users can see their archived items from the archive URL and the EV thick client on their desktops. This mail app gives more comfort for the end users to access, make operations on their archive from the owa and viewing their email on outlook itself.
2) Support for the Enterprise Vault Office Mail App is pending from Exchange 2016 CU1 and not in Symantec compatibility lists.At this moment the Office mail app is working only on owa in Exchange 2016 CU2. Symantec has confirmed that they will be soon releasing a patch which will support this feature on Outlook as well.
3) With Exchange 2016 CU2 Archive is working fine on the Outlook EV Client and the EV Web URL.
4) Enterprise vault to be compatible with Exchange 2016 Cu2 server version requires Enterprise Vault 11.0.1 Cumulative Hotfix 4 or later.
Below are the following commands are available for managing Office
Mail Apps in Exchange 2016:
Get-App – Returns information about the installed Office Mail Apps.
New-App – Deploys an Office Mail App.
Remove-App – Removes the specified Office Mail App.
Disable-App – Disables a specific Office Mail App for a specific user.
Enable-App – Enables an Office Mail App for a specific user.
Set-App – Sets configuration properties on an Office Mail App.
Thanks & Regards
Sathish Veerapandian
MVP – Office Servers and Services